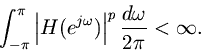NOTE: THIS DOCUMENT IS OBSOLETE, PLEASE CHECK THE NEW VERSION: "Introduction to Digital Filters with Audio Applications", by Julius O. Smith III, Copyright © 2017-11-26 by Julius O. Smith III - Center for Computer Research in Music and Acoustics (CCRMA), Stanford University
<< Previous page TOC INDEX Next page >>
Vector Space Concepts
Definition. A set
of objects is called a metric spaceif with any two points
and
of
there is associated a real number
, called the distance from
to
, such that (a)
if
;
, (b)
, (c)
, for any
[Rudin 1964].
Definition. A linear space is a set of ``vectors''
together with a field of ``scalars''
with an addition operation
, and a multiplication opration
taking
, with the following properties: If
,
, and
are in
, and
are in
, then
The element
.
.
- There exists
in
such that
for all
in
.
.
.
.
.
is written as
thus coinciding with the notation for the real number zero. A linear space is sometimes be called a linear vector space, or a vector space.
Definition. A normed linear space is a linear space
on which there is defined a real-valued function of
called a norm, denoted
, satisfying the following three properties:
The functional
, and
.
,
a scalar.
.
serves as a distance function on
, so a normed linear space is also a metric space.
Note that when
is the space of continuous complex functions on the unit circle in the complex plane, the norm of a function is not changed when multiplied by a function of modulus
on the unit circle. In signal processing terms, the norm is insensitive to multiplication by a unity-gain allpass filter (also known as a Blaschke product).
Definition. A pseudo-norm is a real-valued function of
satisfying the following three properties:
A pseudo-norm differs from a norm in that the pseudo-norm can be zero for nonzero vectors (functions).
, and
.
,
a scalar.
.
Definition. A Banach Space is a complete normed linear space, that is, a normed linear space in which every Cauchy sequence2*A sequence
is said to be a Cauchy sequence if for each
there is an
such that
for all
and
larger than
. converges to an element of the space.
Definition. A function
is said to belong to the space
if
Definition. A function
is said to belong to the space
if it is in
and if its analytic continuation
is analytic for
.
is said to be in
if
.
Theorem. (Riesz-Fischer) The
spaces are complete.Proof. See Royden [Royden 1968], p. 117.
Definition. A Hilbert space is a Banach space with a symmetric bilinearinner product
defined such that the inner product of a vector with itself is the square of its norm
.