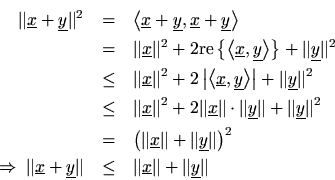NOTE: THIS DOCUMENT IS OBSOLETE, PLEASE CHECK THE NEW VERSION: "Mathematics of the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT), with Audio Applications --- Second Edition", by Julius O. Smith III, W3K Publishing, 2007, ISBN 978-0-9745607-4-8. - Copyright © 2017-09-28 by Julius O. Smith III - Center for Computer Research in Music and Acoustics (CCRMA), Stanford University
<< Previous page TOC INDEX Next page >>
Triangle Inequality
The triangle inequality states that the length of any side of a triangle is less than or equal to the sum of the lengths of the other two sides, with equality occurring only when the triangle degenerates to a line. In
, this becomes
We can show this quickly using the Schwarz Inequality.