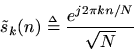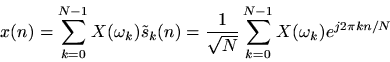NOTE: THIS DOCUMENT IS OBSOLETE, PLEASE CHECK THE NEW VERSION: "Mathematics of the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT), with Audio Applications --- Second Edition", by Julius O. Smith III, W3K Publishing, 2007, ISBN 978-0-9745607-4-8. - Copyright © 2017-09-28 by Julius O. Smith III - Center for Computer Research in Music and Acoustics (CCRMA), Stanford University
<< Previous page TOC INDEX Next page >>
Normalized DFT
A more ''theoretically clean'' DFT is obtained by projecting onto thenormalized DFT sinusoids
In this case, the normalized DFT ofis
which is also precisely the coefficient of projection ofonto
. The inverse normalized DFT is then more simply
While this definition is much cleaner from a ''geometric signal theory'' point of view, it is rarely used in practice since it requires more computation than the typical definition. However, note that the only difference between the forward and inverse transforms in this case is the sign of the exponent in the kernel.