NOTE: THIS DOCUMENT IS OBSOLETE, PLEASE CHECK THE NEW VERSION: "Mathematics of the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT), with Audio Applications --- Second Edition", by Julius O. Smith III, W3K Publishing, 2007, ISBN 978-0-9745607-4-8. - Copyright © 2017-09-28 by Julius O. Smith III - Center for Computer Research in Music and Acoustics (CCRMA), Stanford University
<< Previous page TOC INDEX Next page >>
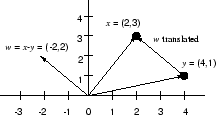
Vector Subtraction
Figure 6.7 illustrates the vector difference
between
and
. From the coordinates, we compute
.
Note that the difference vector
may be drawn from the tip of
to the tip of
rather than from the origin to the point
; this is a customary practice which emphasizes relationships among vectors, but the translation in the plot has no effect on the mathematical definition or properties of the vector. Subtraction, however, is not commutative.
To ascertain the proper orientation of the difference vector
, rewrite its definition as
, and then it is clear that the vector
should be the sum of vectors
and
, hence the arrowhead is on the correct endpoint.